Abstract on paediatric solid oral dosage forms
There is a growing interest in enhancing the acceptability of paediatric pharmaceutical formulations. Solid oral dosage forms (SODF), especially multiparticulates, are being considered as an alternative to liquid formulations, but they may compromise palatability when large volumes are required for dosing. We hypothesised that a binary mixture of multiparticulates for paediatric use, designed to increase the formulation maximum packing fraction, could reduce the viscosity of the mixture in soft food and facilitate swallowing.
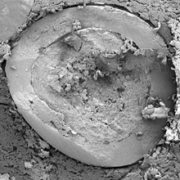
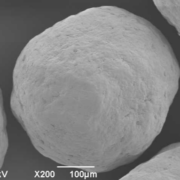
Using the Paediatric Soft Robotic Tongue (PSRT) – an in vitro device inspired by the anatomy and physiology of 2-year-old children – we investigated the oral phase of swallowing for multi-particulate formulations, i.e., pellets (350 and 700 µm particles), minitablets (MTs, 1.8 mm), and their binary mixtures (BM), by evaluating oral swallowing time, the percentage of particles swallowed, and post-swallow residues. We also conducted a systematic analysis of the effect of the administration method, bolus volume, carrier type, particle size, and particle volume fraction on pellets swallowability.
The results demonstrated that the introduction of pellets affected the flowing ability of the carriers, increasing shear viscosity. The size of the pellets did not appear to influence particle swallowability but raising the particle volume fraction (v.f.) above 10% resulted in a decrease in the percentage of particles swallowed. At v.f. 0.4, pellets were easier to swallow (+ 13.1%) than MTs, being the administration method used highly dependent on the characteristics of the multi-particulate formulation under consideration. Finally, mixing MTs with only 24% of pellets improved particle swallowability, achieving swallowing levels similar to those of pellets alone. Thus, combining SODF, i.e., MTs and pellets, improves MT swallowability, and offers new possibilities for adjusting product palatability, being particularly attractive for combination products.
Authors: Alejandro Avila-Sierra, Anais Lavoisier, Carsten Timpe, Peter Kuehl, Leonie Wagner, Carole Tournier, Marco Ramaioli
Read more
Get the full publication on paediatric solid oral dosage forms by Alejandro Avila-Sierra et al. here. Used MCC pellet: Cellets 350 and Cellets 700.


 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharm 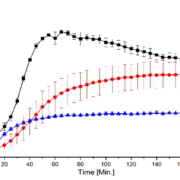
 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharm  Ingredientpharm
Ingredientpharm  ingredientpharm
ingredientpharm 
 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharm