Case Studies
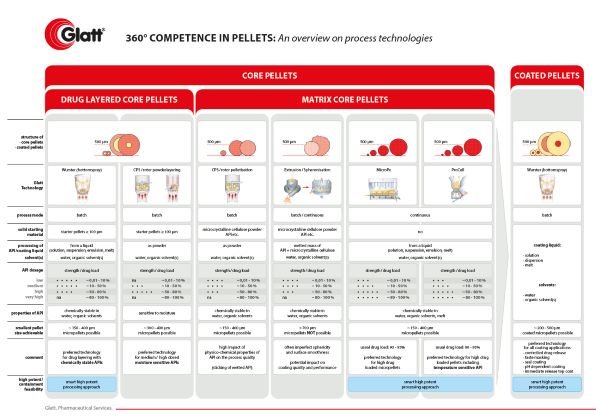 Glatt
https://cellets.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/pellets_overview_technologies_small.jpg
418
596
Bastian Arlt
https://cellets.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Logo_Cellets_2016_website.png
Bastian Arlt2024-06-28 14:11:202023-08-02 16:51:39Download center
Glatt
https://cellets.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/pellets_overview_technologies_small.jpg
418
596
Bastian Arlt
https://cellets.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Logo_Cellets_2016_website.png
Bastian Arlt2024-06-28 14:11:202023-08-02 16:51:39Download center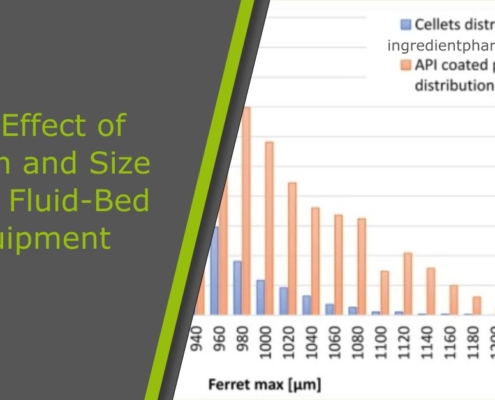
The Effect of Design and Size of the Fluid-Bed Equipment on the Particle Size-Dependent Trend of Particle Coating Thickness and Drug Prolonged-Release Profile
Abstract
The focus of the current work is to study and demonstrate the impact of the design, the scale, and settings of fluid-bed coating equipment on the differences in pellet coating thickness, which in case of prolonged-release pellets…
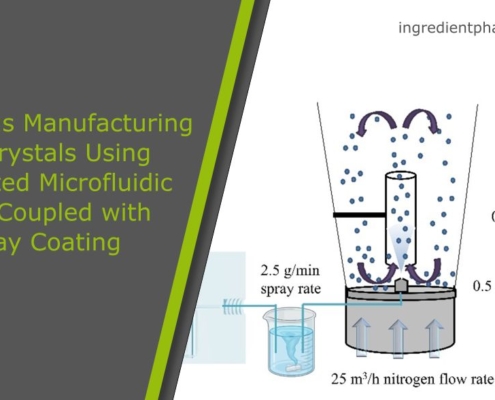
Continuous Manufacturing of Cocrystals Using 3D-Printed Microfluidic Chips Coupled with Spray Coating
Abstract on Continuous Manufacturing
Using cocrystals has emerged as a promising strategy to improve the physicochemical properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) by forming a new crystalline phase from two or more components.…

Scientific literature on MCC pellets (CELLETS)
Selected Scientific literature
Please, find scientific literature on CELLETS®, MCC spheres. This list is constantly updated and does not claim to be complete. If you are author, scientist or R&D specialist, please submit your present publication…

Modelling the disintegration of pharmaceutical tablets: integrating a single particle swelling model with the discrete element method
 ingredientpharm
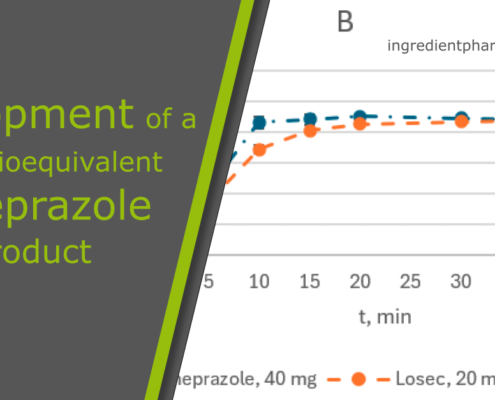
ingredientpharmDevelopment of a New Bioequivalent Omeprazole Product
The publication by G. Kumisbek, D. Vetchý, A. Kadyrbay describes gently the development and implementation of a new generic enteric form of CELLETS® 700 (MCC pellets, 700-1000 µm) loaded with omeprazole in capsules by Viva Pharm LLP, a pharmaceutical…
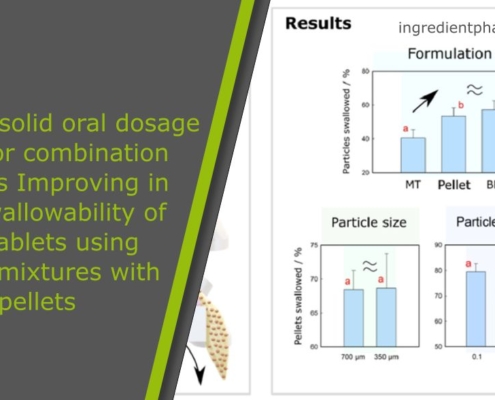
Paediatric solid oral dosage forms for combination products: Improving in vitro swallowability of minitablets using binary mixtures with pellets
Abstract on paediatric solid oral dosage forms
There is a growing interest in enhancing the acceptability of paediatric pharmaceutical formulations. Solid oral dosage forms (SODF), especially multiparticulates, are being considered as an…
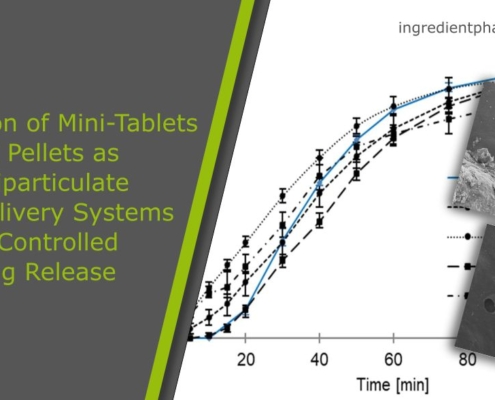
Comparison of Mini-Tablets and Pellets as Multiparticulate Drug Delivery Systems for Controlled Drug Release
Abstract
Mini-tablets made into hard capsules or administered using special dosing units, as well as pellets in hard capsules or compressed into tablets, offer the advantages of multiparticulate drug delivery systems and are suitable for controlled…
Investigating the Influence of Fluid-Bed Equipment Design and Size on Particle Coating Thickness Trends and Drug Prolonged-Release Profiles Linked to Particle Size
The primary objective of this research is to investigate the design and size on particle coating thickness. Furthermore, illustrate how the design, size, and configurations of fluid-bed coating machinery influence variations in pellet coating…
 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharmCritical aspects of starter spheres in oral pellet formulations one should consider
 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharmPreparation and characterization of controlled-release doxazosin mesylate pellets using a simple drug layering-aquacoating technique
Abstract
Pellets are one of multiparticulate pharmaceutical forms and can offer numerous technical and biopharmaceutical advantages compared with single dose unit formulations, e.g. tablets and capsules. This study aimed at formulation…
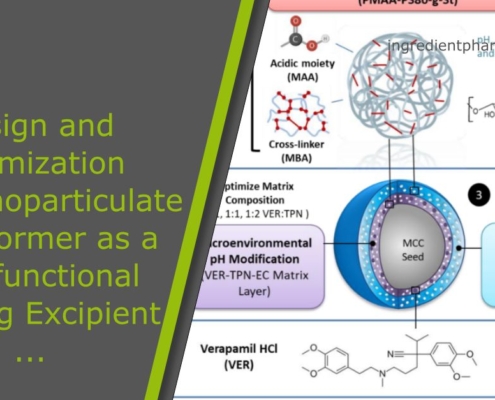
Design and Optimization of a Nanoparticulate Pore Former as a Multifunctional Coating Excipient for pH Transition-Independent Controlled Release of Weakly Basic Drugs for Oral Drug Delivery
Abstract
Bioavailability of weakly basic drugs may be disrupted by dramatic pH changes or unexpected pH alterations in the gastrointestinal tract. Conventional organic acids or enteric coating polymers cannot address this problem adequately…

Amorphous Solid Dispersions Layered onto Pellets – An Alternative to Spray Drying?
This article "Amorphous Solid Dispersions Layered onto Pellets - An Alternative to Spray Drying?" is an excerpt from the publication of Neuwirth et al., Pharmaceutics 2023, 15(3), 764; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030764.
Abstract
Spray…
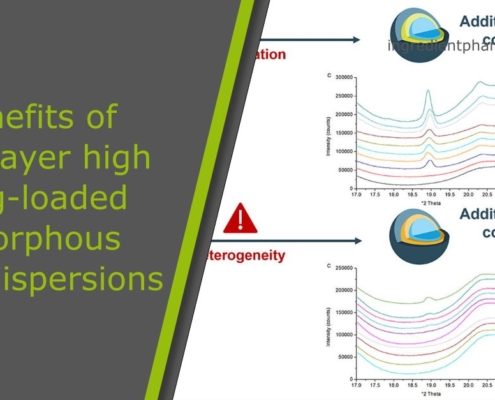
Benefits and challenges of multilayer high drug-loaded amorphous solid dispersions
Introduction on amorphous solid dispersions
What is the benefit of multilayer amorphous solid dispersions? Recently, several studies had been performed on amorphous solid dispersions working spheres or starter beads. Starter beads, such as…
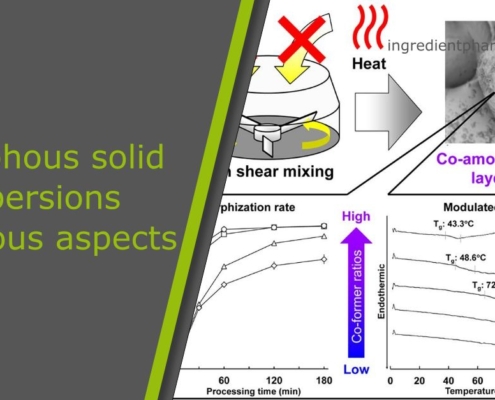 ingredient pharm
ingredient pharmAmorphous solid dispersions at various aspects
We identified, that amorphous solid dispersions gain in importance as they increase the solubility and dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs. There are severall attempts, in which each of them positive aspects and certain issues occur.…
 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharmHydrodynamic behavior of MCC Spheres in a spouted bed
Abstract
This case study is a short abstract on spouted bed characteristics, following closely findings in the publication by J. Vanamu and A. Sahoo [1].
Spouted bed systems are of highest importance for all powder processing industries,…
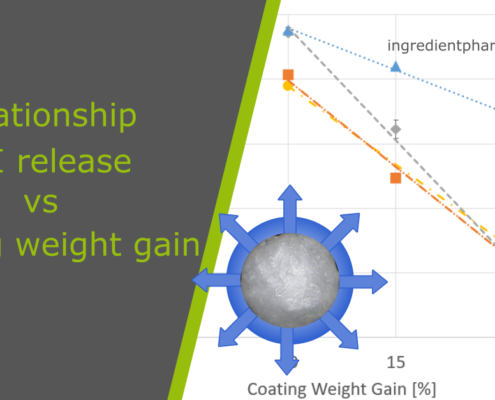 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharmCoating weight gain and API release in multiparticulates
Abstract
Multiparticulates made of pellets are ideal dosage forms to be used in pediatrics. Having the suitability of paediatric consumers in mind, formulations of small-sized pellets offer a valuable base for increased compliance and improved…
Metoprolol Tartrate: controlled release drug layered pellets for colon-specific drug delivery
Abstract on Metoprolol pellets
Metoprolol Tartrate is a salt of Metoprolol, a selective β1-receptor blocker medication. The application is the treatment of high blood pressure, chest pain due to poor blood flow to the heart, and several conditions…
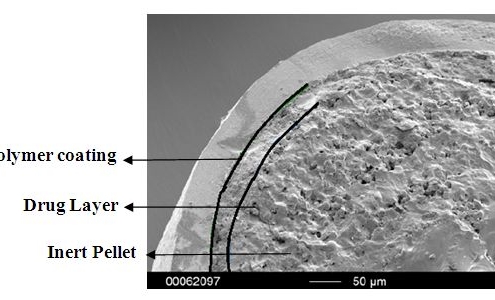
Atomoxetine HCl Pellets in MUPS Formulations
Abstract
This case study on Atomoxetine HCl pellets is a short abstract of the publication by Y.D. Priya et al. [1].
Atomoxetine is a medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [2]. The API is marketed under…

Tamoxifen citrate was spray layered micropellets for Cre recombination research
Abstract on Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen is widely used in transgenic research in mice to induce Cre recombinase activity and achieve conditional gene knockouts [1]. However administrating tamoxifen to mice is challenging The commonly used dosing methods…
 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharmBSC Class I APIs in oral formulations
 Ingredient Pharm
Ingredient PharmTechnologies for enhancing bioavailability of Simvastatin
Abstract
This application note is based on content from Pohlen et al. [1]. Simvastatin (CAS number 79902-63-9) is a cholesterol-lowering agent with a low bioavailability of 5% [2,3]. This API is formulated as a lipid based drug delivery system…
Multidimensional Correlation of Surface Smoothness and Process Conditions
Abstract
Multidimensional Correlation of Surface Smoothness and Process Conditions is a necessary attempt to better understand, optimize and outperform process steps of drug formulations. Particle coating and layering in a fluidized bed process…

Gliclazide formulations for Sustained Release Delivery
Abstract
Patients with dysphagia may have obstacles to swallow tablets or large multiparticulates. The former dosage form can even not be crushed in case that the tablet exhibits a modified release or taste-masking profile through outer layering.…
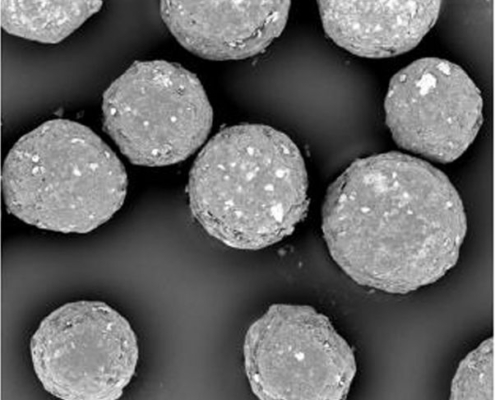
Microparticle coating in Wurster Fluidized Bed – Scalable Production of Oral Sustained-Release Drugs
Abstract
Modified drug release formulations for suspensions are a perfect solution for children and patients with swallowing difficulties. In many cases, these formulations are based on pellets serving as starter beads. In this report, an attempt…
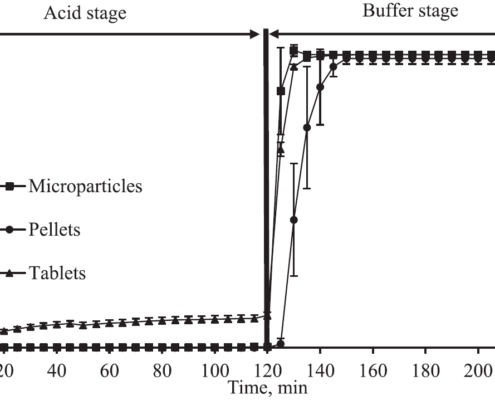
Faster drug release of enteric coated microparticles in bicarbonate buffers media
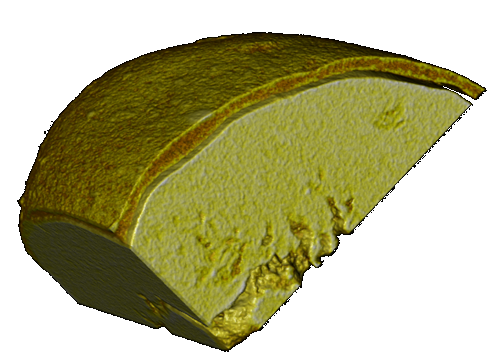
Coating uniformity of hot-melt coated particles
Abstract
Coating uniformity is a critical parameter in coating processes in novel pharmaceutical formulations. Speaking about pellet technology, coating and layering are the main methods for implementing drug functionalities, such as modified…
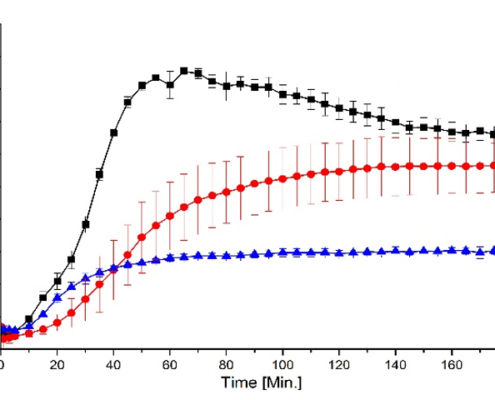
Amorphous solid dispersions layered pellets
Abstract
Amorphous solid dispersions layered pellets solve a problem of poorly water soluble drugs. Speaking about oral drug formulations, drug carrier solutions based on starter cores are suitable for several drug classes and open new opportunities…
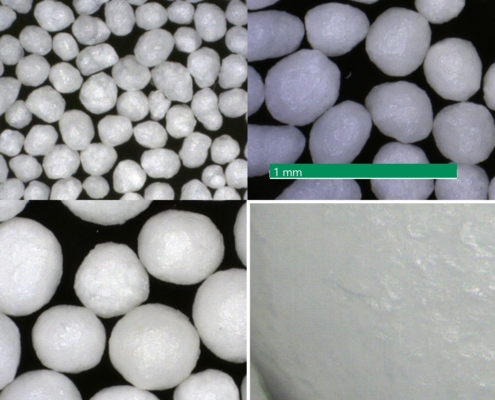 Ingredientpharm
IngredientpharmImpact of the particle size on powder behavior in a Wurster fluid-bed process
Abstract
Cellets are inert starter cores made of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). They play an important role in new formulations of solid dosage forms. As a carrier system for actives, the chemical inertness and surface smoothness are crucial…
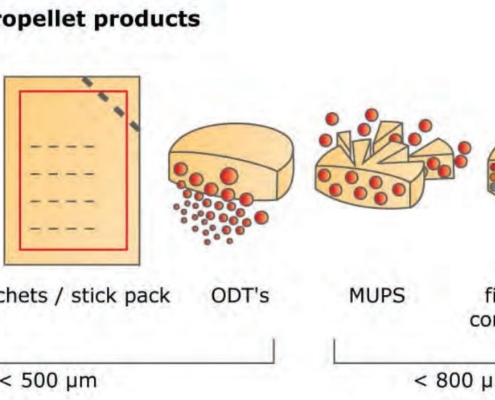 glatt.com
glatt.comThe path to the perfect sphere
The renaissance of micropellets is promoting innovative technologies
In recent years, formulations based on pellets and micropellets have been the trend. New technologies make it possible to circumvent property rights for active ingredients…
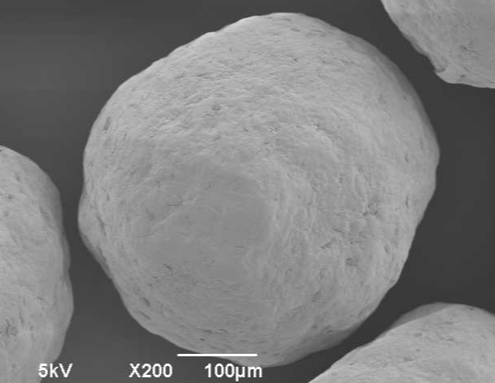 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharmSome light on sugar and microcrystalline cellulose pellets
Abstract
Microcrystalline cellulose pellets (MCC) and sugar are well-known materials in pellet technology. Pellet technology describes the drug load onto starter pellets for controlled release formulations by Wurster process or others. Inert…
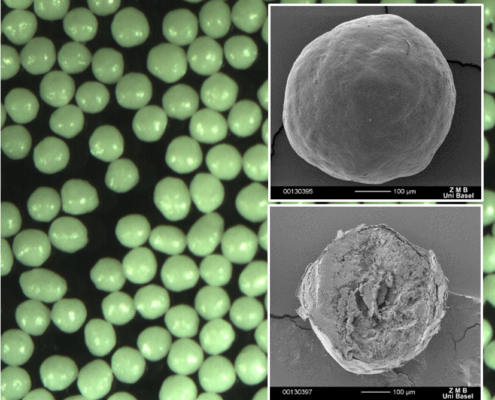 https://cellets.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/CS_hydrocortisone_image_5.png
699
827
Bastian Arlt
https://cellets.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Logo_Cellets_2016_website.png
Bastian Arlt2021-03-04 13:01:512023-07-06 14:55:59Case Study: Hydrocortisone for paediatrics
https://cellets.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/CS_hydrocortisone_image_5.png
699
827
Bastian Arlt
https://cellets.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Logo_Cellets_2016_website.png
Bastian Arlt2021-03-04 13:01:512023-07-06 14:55:59Case Study: Hydrocortisone for paediatrics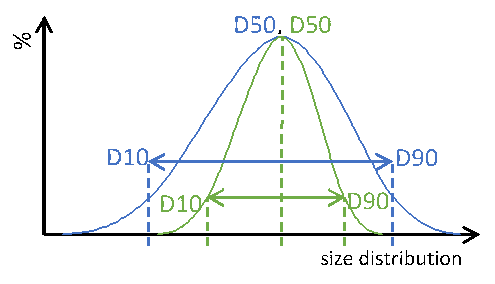
Sphericity and size distribution of µm-sized microcrystalline pellets
Abstract
Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) pellets represent a chemically inert class of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) carriers. A narrow particle size distribution (PSD) maximizes control over content uniformity. In this case study,…
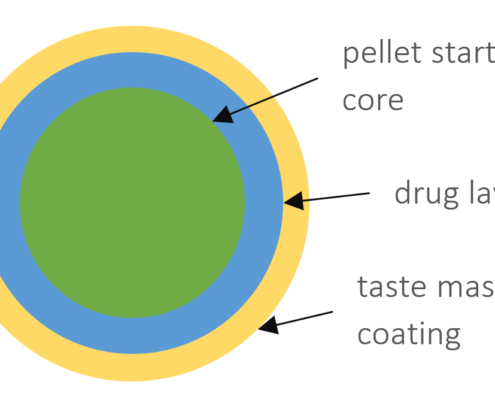
Taste-masked cellulose based pellets for compaction
Abstract
Several drug substances are known to be extremely bitter. In special for paediatric and geriatric applications, costumer compliance by means of taste acceptance is a highly sensitive topic. Taste masking is therefore an important issue…

Better MUPS tablets: Aspects of MCC starter beads
Abstract
Starter beads such as pellets made of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) are frequently used in the formulation of oral drug delivery systems, e.g. multiparticulates [1] or multi-unit pellet system (MUPS) tablets [2]. Certain properties…

Case Study: Layering of Theophylline
Abstract
Theophylline is a powerful active used for the acute treatment of respiratory distress. Its bioavailability and uptake rates are high. Drug carrier systems are pellets made of sugar or microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). This case study…
