Abstract
Starter beads such as pellets made of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) are frequently used in the formulation of oral drug delivery systems, e.g. multiparticulates [1] or multi-unit pellet system (MUPS) tablets [2]. Certain properties are requested to MCC pellets. We shed some light on sphericity size and friability in this note.
Starter beads for MUPS tablets
MUPS tablets consist of pellets which are compressed – assisted by excipients such as disintegrants and fillers. The pellets used are usually functional coated to achieve desired drug release profiles.
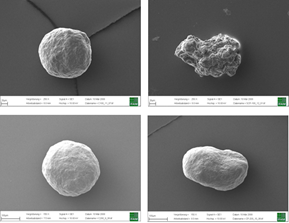
Top: Inert Cellets® 100 (100-200 µm, left) in comparison with another MCC sphere (75-212 µm, right). Bottom: Inert Cellets® 200 (200-350 µm, left) in comparison with another MCC sphere (150-300 µm).
Figure 1: Top: Inert Cellets® 100 (100-200 µm, left) in comparison with another MCC sphere (75-212 µm, right). Bottom: Inert Cellets® 200 (200-350 µm, left) in comparison with another MCC sphere (150-300 µm).
The characteristics of the starter bead as a neutral carrier should therefore include high sphericity (Figure 1), constant particle size distribution and smooth surface. These aspects count especially for the formulation of low dosed highly active APIs.
For the application in MUPS tablets small size and high mechanical stability (low friability) are of interest to achieve desired drug loading and avoid film damage during compression.
Size
Any question relating to optimized drug load and coating layers of pellets is a question of size and sphericity of the starter beads.
So, what is the main influence of size? Size needs to be considered for achieving desired drug load in relation to a total dimension of the pellet. While the total dimension of the pellet is mainly defined by the application – e.g. processing as a capsule, tablet or sachet –, the initial pellet size defines the maximum thickness of coating levels (Figure 2). Size might also be a matter of content uniformity with low dosed API and also needs to be mentioned by means of processability, which is in particular electrostatic loading or sticking. Particle size distribution influences the dissolution profile.

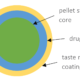
Figure 2: Sketch of a functionally coated pellet. The size of the initial pellet (green) defines the maximum thickness of all coating layers (blue) which may contain API and excipients, as well.
Figure 2: Sketch of a functionally coated pellet. The size of the initial pellet (green) defines the maximum thickness of all coating layers (blue) which may contain API and excipients, as well.
Sphericity
Sphericity is a strong parameter which influence depends on drug loading and coating levels. Also for the control of dissolution profile where specific surface area and content uniformity play important roles, the influence of sphericity needs to be understood (Figure 3). Please do not forget, that with decreasing sphericity, the flow probabilities of powders are decreasing (powder rheology), which might affect process properties such as powder transport.

Figure 3: Sketch of non-spherical starter beads (green) with coating layers (blue). Coating layer thickness and dissolution profiles are hard to control in this case.
Figure 3: Sketch of non-spherical starter beads (green) with coating layers (blue). Coating layer thickness and dissolution profiles are hard to control in this case.
Thus, starter beads of uniform size (distribution) and sphericity are the better solution for overcoming these issues by simplifying drug formulation and processing. Such starter beads can be pellets of MCC, sugar or tartaric acid. MCC pellets surely show perfect initial conditions as they exhibit chemical inertness and therefore can be combined with several APIs. In case of weakly basic APIs, tartaric acid pellets are advantageous.

Figure 4: A pellet inside a compressed MUPS tablet. The starter bead is surrounded by a coating layer of exemplarily excipient or API. A powdery excipients matrix surrounds the coated pellet. Friability is absolutely low.
Figure 4: A pellet inside a compressed MUPS tablet. The starter bead is surrounded by a coating layer of exemplarily excipient or API. A powdery excipients matrix surrounds the coated pellet. Friability is absolutely low.
Figure 4 shows a cross-section of a pellet in the matrix of a compressed MUPS tablet. It is mentionable, that due to low friability a high degree of sphericity as well as surface smoothness are kept after compression and film damage of coating layers is not identified.
Summary
Cellets® offer a perfect combination of chemical inertness towards the selection of the API and physical properties that allow optimized and stable processing in a fluid bed process for layering and coating of the starter beads. Main advantages are the low friability, smooth surface, sphericity and narrow size distributions.
Cellets® starter beads therefore provide excellent conditions for controlled drug dissolution profiles.
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge Fraunhofer IFAM (Dresden, Germany) for providing electron microscopic images.
References
[1] Pöllinger N, Drug Product Development for Older Adults—Multiparticulate Formulations. In: Stegemann S. (eds) Developing Drug Products in an Aging Society. AAPS Advances in the Pharmaceutical Sciences Series, vol 26 (2016). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-43099-7_16
[2] Bhad ME, Abdul S, Jaiswal SB, Chandewar AV, Jain JM, Sakarkar DM. MUPS tablets—a brief review. Int J Pharm Tech Res. 2010;2:847–55




 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharm 
 ingredientpharm
ingredientpharm