The patent application US20240139215A1 focuses on the development of controlled release formulations for highly lipophilic physiologically active substances, such as cannabinoids. These substances tend to have high lipid solubility (log P of 4 or more), making them difficult to deliver in a controlled and effective manner. This patent addresses the need for efficient controlled release systems that can provide consistent therapeutic effects by utilizing a matrix-based approach.
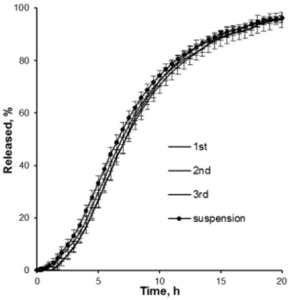
The formulation includes a matrix that contains one or more highly lipophilic active substances and water-soluble binders like hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), methyl cellulose (MC), or similar polymers. The key challenge with such substances is their tendency to release slowly and incompletely when taken orally, which this patent solves by adjusting the proportion of water-soluble binders. The binder content is carefully selected to be between 0.1-10% of the total matrix weight, optimizing the release rate of the active substances over the gastrointestinal transit time.
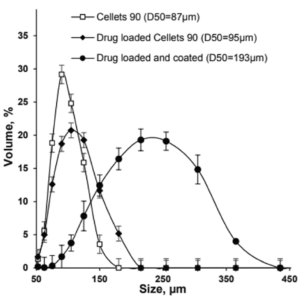
One of the innovative aspects of the invention is the use of matrix pellets, which are small particles with a size range of 30 µm to 1800 µm. These pellets may be administered in various forms, such as capsules, tablets, or sachets. The flexibility of the dosage forms makes it easier to control and adjust the release kinetics of the active ingredients.
The CELLETS® play a crucial role in this formulation. They are used as neutral cores for the deposition of the active substances and their binders. CELLETS® are microcrystalline cellulose spheres that provide an ideal substrate for layering the active substance and polymers, ensuring uniform distribution and controlled release. By using these CELLETS®, the formulation can achieve a more predictable and consistent release profile, crucial for substances like cannabinoids that require precise dosing to avoid psychoactive side effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
Additionally, these pellets can be coated with other materials to further control the release rate if desired, though this is optional. In many embodiments, the matrix pellets themselves are sufficient to achieve the desired controlled release without the need for additional coatings.
In conclusion, the US20240139215A1 patent introduces a novel approach to the controlled release of highly lipophilic substances, leveraging matrix technology with carefully chosen water-soluble binders and neutral cores like CELLETS®. This method ensures effective delivery and consistent release, addressing the challenges posed by the lipophilic nature of substances like cannabinoids. In this specific patent, the following MCC Sphere types are recommended: CELLETS® 500.
Document information
Inventors:
Jay Jesko Nowak
Annette Grave
Monika Wentzlaff
Sarah Barthold
Christian Geugelin
Disclaimer
This text was generated by chatGPT engine version GPT‑4o, on Oct 21, 2024. Image was generated with Adobe Firefly.

 adobe firefly
adobe firefly